|
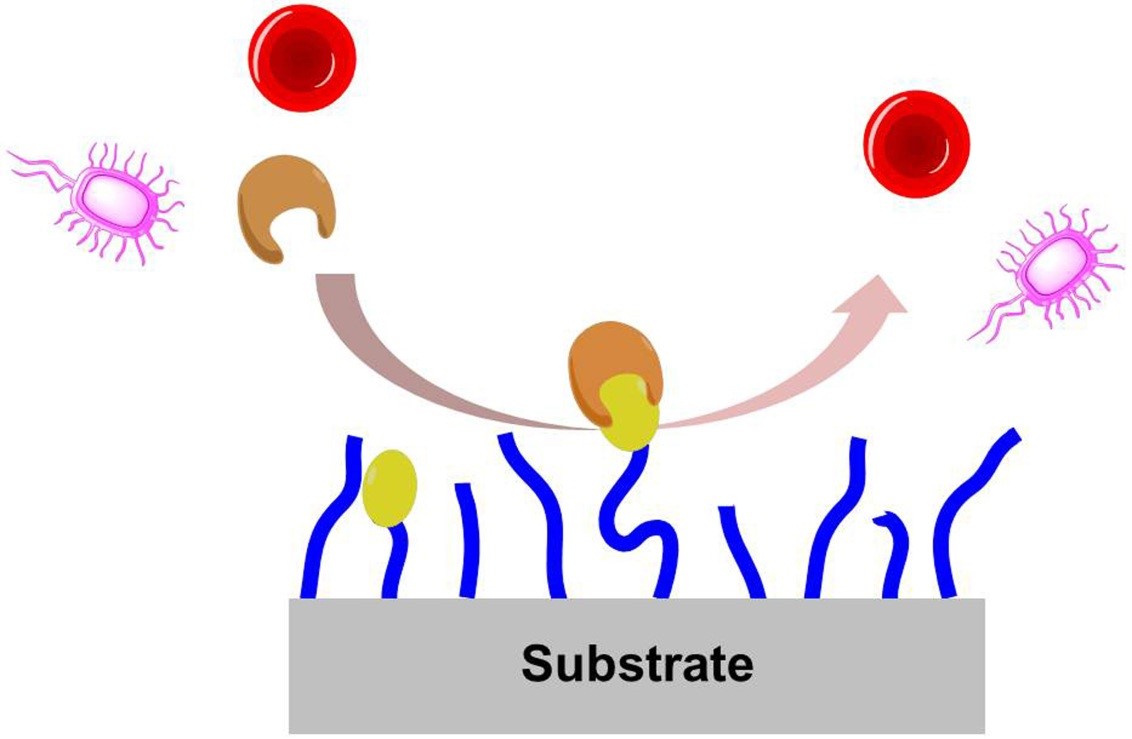
Biofouling, the deterioration of device and surface function resulting from the accumulation of biological matter (i.e., proteins, cells, and microorganisms), is an important issue in a wide range of fields, including biosensors, biomedical devices, medical implants, marine equipment, water purification, and drug delivery carriers.1 Given the fact that the biofouling is a universal and problematic phenomenon, such as low signal-to-noise ratios for immunoassays and harmful side effect for biological implants, it is necessary to introduce functionalities on solid surfaces (e.g., silicone, gold, and polymer surfaces), which minimize the unwanted, non-specific adsorption of bioentities as well as improve the device function.2 Therefore, many studies have been reported how to reduce the nonspecific adsorption of bioentities on the surfaces. Recently, it has been found that non-biofouling coating on biocompatible polymers, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) derivatives and zwitterionic polymers, is one of the best methods to minimize the biofouling on solid surfaces as shown in Figure 1.3,4 Herein, we present non-biofouling polymer coatings polymerization on gold, silicone and cyclic olefin copolymer surfaces, using surface organic reactions and surface-initiated, atom transfer radical polymerization. The formed polymeric coated substrates are characterized by water contact angle, ellipsometric thickness, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Moreover, the non-biofouling performance of the substrates is investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and fluorescent microscopy. We believe that the strategy used herein will not only widen the application of non-biofouling coating on solid surfaces to biosensors and medical devices, but also be applicable to various other substrates which need to be functionalized spatioselectively for their applications. |
|
 120th General Meeting of the KCS
120th General Meeting of the KCS
 120th General Meeting of the KCS
120th General Meeting of the KCS