|

|
| Type |
Poster Presentation |
| Area |
Material Chemistry |
| Room No. |
Exhibition Hall 2+3 |
| Time |
10월 19일 (목요일) 11:00~12:30 |
| Code |
MAT.P-389 |
| Subject |
A fluorescence carbon dot using nitrogen containing compound for bio imaging
|
| Authors |
KyungKwan Lee, Chang-Soo Lee1,*, Chul Soon Park2
Hazards Monitoring Bionano Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & Biotechno, Korea
1Center for Bio Nano Research, Hazards Monitoring Bionano Research Center, Korea
2Polymer?Engineering, Chonnam National University, Korea
|
| Abstract |
|
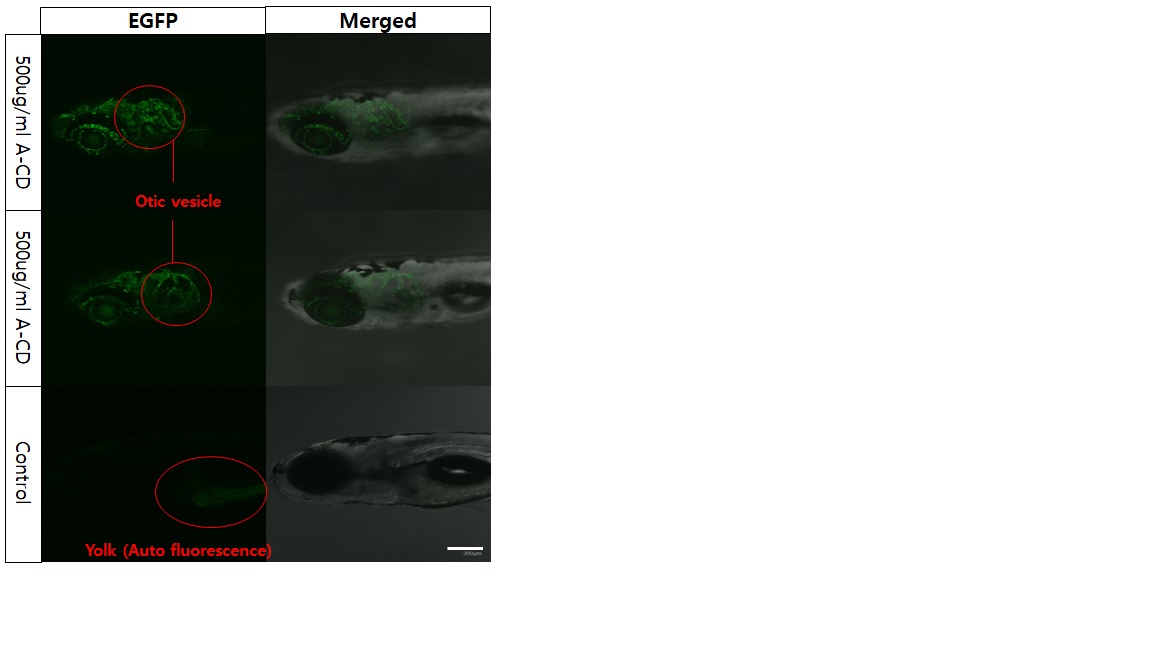
We synthesized hydrothermally water-soluble A-CD(Alendronate-based carbon dots) using commercial osteoporosis medicine. Alendronate as the start material having Bisphosphonate group was used for osteoporosis treatment clinically and also are good candidates as a bone-imaging agent because of high affinity for Hydroxyapatite. A-CD were made from Bisphosphonate derivatives containing nitrogen compound as the source of carbon without surface passivation agent by hydrothermal method. We confirmed that they exhibited the highest fluorescence intensity at 405nm and good photo stability in DI-Water. Due to superior biocompatibility, A-CDs were imaging in living HeLa cells, which indicated that it is applicable in various fields of bio imaging. The high affinity of A-CD for hydroxyapatite also were verified through α-TCP(tri-calcium phosphate) scaffold incubated in A-CDs solution. As new fluorescent carbon material, advantages of A-CD include strong fluorescence, water solubility, unnecessary passivating agent, low cytotoxicity and high affinity for hydroxyapatite. These A-CD showed promising bone specific imaging due to their surface phosphonate-group and suitable candidates for the applications in the bio imaging field.
|
|
|
| E-mail |
leepk812@naver.com |
|
 120th General Meeting of the KCS
120th General Meeting of the KCS
 120th General Meeting of the KCS
120th General Meeting of the KCS